18
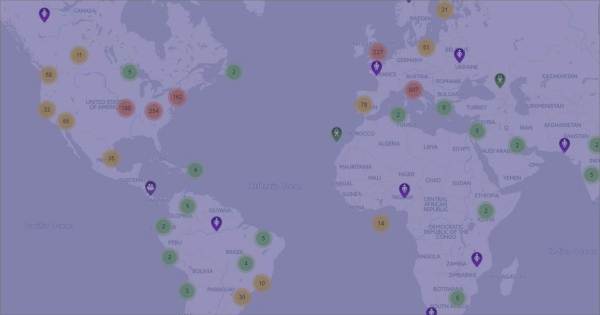
What is the prevalence of Leukodystrophy?
How many people does Leukodystrophy affect? Does it have the same prevalence in men and women? And in the different countries?

The frequency of two common disease-associated mutations in the arylsulphatase A (ASA) gene, and of a mutation causing ASA pseudodeficiency, have been established in metachromatic leukodystrophy patients diagnosed in our laboratory. A total of 37 mutant genes have been analysed. The G→A change destroying the splice donor site of exon 2 is generally associated with more severe disease and was found in 43.2% of mutant ASA genes. The C→T transition causing a proline to leucine substitution at position 426 in exon 8 (P426→L) is associated with later onset disease, and was found in 16.2% of mutant genes. The A→G transition leading to loss of a polyadenylation signal associated with ASA pseudodeficiency was present at a frequency of 7.5% in the patients and heterozygotes studied.
Posted Aug 7, 2017 by Todd 2340